Syllabus (Fourth Edition, 2023)
Topics
i. Outline the methods for assessing coagulation (including TEG and ROTEM).
ii. Outline the methods for assessing platelet function and fibrinolysis.
Topics not covered in previous SAQs
ii. Outline the methods for assessing platelet function and fibrinolysis.
Learning Objectives for the First Part Examination in Intensive Care Medicine
- This will ensure that trainees, tutors, and examiners can work from a common base.
- All examination questions are based around this Syllabus.
- These learning objectives are designed to outline the minimum level of understanding required for each topic.
- The accompanying texts are recommended on the basis that the material contained within them provides sufficient information for trainees to meet the learning objectives.
- Trainees are strongly encouraged to explore the existing and evolving body of knowledge of the Basic Sciences as they apply to Intensive Care Medicine by reading widely.
- For all sections of the syllabus an understanding of normal physiology and physiology at extremes of age, obesity, pregnancy (including foetal) and disease (particularly critical illness) is expected.
- Similarly, for pharmacology, trainees are expected to understand a drug’s pharmacology in these contexts.
- An understanding of potential toxicity and relevant antidotes is also expected.
Definitions
Throughout the document specific wording has been used under the required abilities to indicate the level of knowledge and understanding expected and a glossary of these terms is provided.
Definitions
| Calculate | Work out or estimate using mathematical principles. |
| Classify | Divide into categories; organise, arrange. |
| Compare and contrast | Examine similarities and differences. |
| Define | Give the precise meaning. |
| Describe | Give a detailed account of. |
| Explain | Make plain. |
| Interpret | Explain the meaning or significance. |
| Outline | Provide a summary of the important points. |
| Relate | Show a connection between. |
| Understand | Appreciate the details of; comprehend. |
SAQs
i. Outline the methods for assessing coagulation (including TEG and ROTEM).
2017A 09 – 2014B 08
Outline how the following tests assess coagulation:
a. Prothrombin Time (PT)
b. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
c. Activated Clotting Time (ACT)
d. Thromboelastogram (TEG or ROTEM)
CICMWrecks Answer
Prothrombin Time
Activated partial prothrombin time
What is tested
Extrinsic pathway
Final pathway
Intrinsic pathway
Final pathway
Principles
- Citrate added to chelate calcium
- Sample centrifuged to give plasma
- Calcium returned at time of testing
- Tissue factor added
- Binds to VIIa, activating X
- Time until coagulation measured
- Citrate added to chelate calcium, calcium returned at time of testing
- Sample centrifuged to give plasma
- Calcium returned at time of testing
- Kaolin added
- Activates factor XII
- Cephalin added
- Provides phospholipid surface for binding of tenase and prothrombinase complexes
- Time until coagulation measured
Normal Values
11-13 seconds
30-40 seconds
Causes of Prolonged Time
- Reduction in functional VII
- Warfarin
- Liver disease
- Factor X deficiency
- DIC
Heparin
Haemophilia
DIC
Liver disease
Uses
Warfarin monitoring
Screening test for coagulopathy
Heparin monitoring
Screening test for coagulopathy
Activated clotting time
Thromboelastography
What is tested
Entire clotting cascade and platelet function
Entire clotting cascade and platelet function
Principles
- Whole, fresh blood is added to a clotting activator (e.g. kaolin)
- Time until coagulation measured
- Citrate added to chelate calcium, calcium returned at time of testing
- Sample injected into the sampling cup (containing a clotting activator)
- The cup is rotated around a pin, or the pin rotated independently
- As a clot forms, the pin’s movement is restricted by adherence to it
- This restriction is outputted graphically
Normal values
100-110 seconds
Based on test – TEG/ROTEM
Causes of prolonged time
Any coagulopathy, e.g.
• Clotting factor inhibitors e.g. warfarin, heparin
• Thrombocytopaenia or platelet inhibitors
• DIC
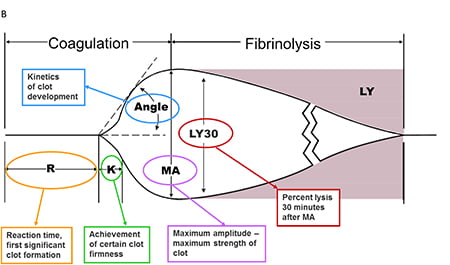
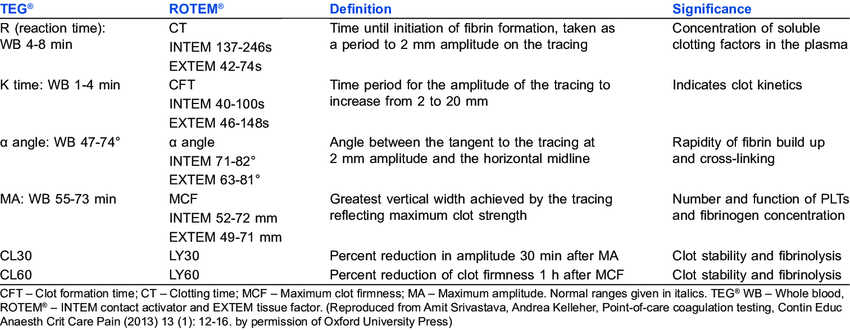
R time – clotting factors
α angle – fibrinogen function and preactivation
MA – platelet number and function
CLT – effectiveness of fibrinolysis
Uses
Monitoring adequacy of coagulation in cardiopulmonary bypass, ECMO, dialysis
Trauma – assess need for blood product replacement
Theatre monitoring
• Cardiac surgery
• Liver transplant
Mooney 2016
Examiner Comments
2017A 09: 61% of candidates passed this question.
Many candidates incorrectly stated that the PT assessed the intrinsic system and that the APTT assessed the extrinsic system. This led to subsequent errors in relating a coagulation test to the appropriate coagulation factors that it assessed. Some candidates produced elaborate diagrams of the coagulation cascade in isolation without relating it to the question.
2014B 08: 0% of candidates passed this question.
It was expected candidates would cover all aspects of testing for each test listed. This would include normal, abnormal or therapeutic values, a comment on methods (either laboratory or point of care) and coagulation pathway assessment. General statements about the overall purpose of the test, collection methods, plasma vs whole blood as sample scored additional marks. Diagnoses or errors associated with abnormalities in each test would also have scored marks but were not mentioned in most answers.
Overall there was a lack of depth of knowledge and incorrect facts. Many candidates knew about TEG, but did not know details about the other tests.

Recent Comments